"Offshore" Geologic History
 |
|
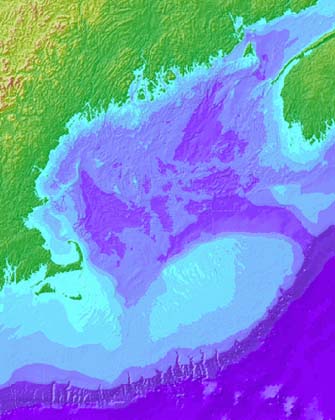
On land and offshore, landforms and bathymetry are usually the result of a long history of geological processes.
For example, color-coded data show how complex landforms in the northeasten U.S. and eastern Canada (greens and yellow, <<<) can extend offshore into Gulf of Maine bathymetry (blues and purples,<<<).
- Click here to see a Gulf of Maine "fly by" movie.
- Bathymetric maps are available for any place on earth at the "Measured and Estimated Seafloor Topography" website.
To learn more about the landforms shown on the map at left (<<<), you can visit our "Geologic History" section.
- For many states in the U.S., you can discover a lot about geology on-line. A good place to begin is the Association of American State Geologists website.
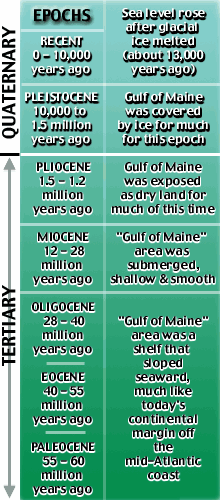
Before we discover which geologic processes formed the complex bathymetric features in the Gulf of Maine, let's consider how geologic time is sub-divided:
- The longest division of geologic time is called an eon.
- The most recent eon, the Phanerozoic, is divided into four eras.
- We're living in the Cenozoic Era.
- A geologic period is shorter: an era contains two or more periods.
- The Cenozoic Era has had two geologic periods: Quaternary and Tertiary (shown at right, >>>).
- The Quaternary Period has had two epochs: Pleistocene and Recent.
Look at the geologic timeline for the Cenozoic Era (right, >>).
- As you go down the geologic timeline, you go back in time (leftmost column). This is based on the principle that, in general, older layers of rock are found buried beneath younger rock layers.
- The rightmost column of the timeline describes the Gulf of Maine's geologic history.
- The Gulf of Maine's coastline has shifted significantly landward
and seaward through geologic history.
- This is because sea level has risen and fallen through time, mostly because of the freezing and melting of glaciers.
- Also, the "land level" has risen and fallen. This is because as glaciers form, they "press down on" or depress the land; as glaciers melt, the land "bounces back" up.
- Geologic timeline and other information are derived from "The Gulf of Maine," by Spencer Apollonio, 1979, Courier of Maine Books (pub.) and Maine Geological Survey's Geologic History on-line "Fact Sheets."
[Click here to see
today's mid-Atlantic contintental margin.]
 |
- Suppose you were told that the same "powerful forces" that shaped many of landforms in eastern Canada and the northeastern U.S. also influenced the bathymetry of the Gulf of Maine.
- Click here to see a larger version of the map.
- Click
here to see the "fly by" movie.
- What similarities between the land topography and Gulf of Maine bathymetry might support this hypothesis?
- What differences between the land topography
and Gulf of Maine bathymetry might NOT support this hypothesis?
- Based on your observations, do you think
the Gulf of Maine bathymetry was mostly "carved" by
glaciers?
- If not, what other processes might have formed features in the Gulf of Maine.
- Based on your observations, do you think
the Gulf of Maine bathymetry was mostly "carved" by
glaciers?
- Click here to see a graph of Gulf of Maine sea level versus time over the past 30,000 years. It shows that about 18,000 years ago sea level began to rise as glaciers melted and returned water to the oceans. If you assume that the "land level" itself was stable and at the same elevation that it is today...
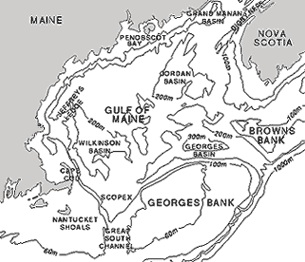
- ...when was Georges Bank exposed?
- ...when was Browns Bank exposed?
- How deep was water in the...
- Jordan Basin...
- Wilkinson Basin...
- and Georges Basins at the beginning of the Recent Epoch?
 |
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
