|
|
MATERIALS
- plastic cake pan
- 16 oz. water or Rheoscopic fluid
- scissors
- sturdy plastic wrap
- tape
- "Physics of the Wave" chart (provided
below)
- (optional) QuickTime animation viewer installed on your computer
|
|
| |
PROCEDURE
|
|
| |
|
|
Activity
- Cut a hole in the bottom of the plastic cake pan approximately
4 inches in diameter.
- Tape plastic wrap on the outside of the plan covering the hole,
making sure it is water tight.
- Fill pan with fluid.
- Gently tap on the plastic wrap on the bottom. What happens?
Why?
- Change the strength of your tap. What
happens?
- Click here to see an animation of
a tsunami.
|
|
| |
Discussion questions
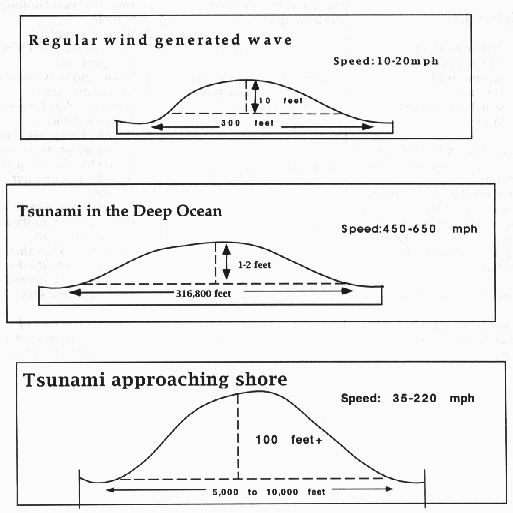
- How fast can tsunamis travel?
- What are typical tsunami wave lengths
and wave periods?
- Click here to see an image of
wave length and wave period.
- What causes tsunamis?
- As wave length increases, what happens to wave velocity?
- Imagine that you live in a coastal community that is susceptible
to tsunamis. What should your community do to mimimize the potential
impact and loss of life?
|
|
|
|
| |
CROSS-CURRICULAR IDEAS
- Mathematics:
- Speed of propagation is V = square-root of (g * h)
- V is the velocity in meters per second
- g is the acceleration of gravity, 9.8 meters per (second)^2
- h is water depth in meters
- If the wave depth is 3000 meters, what is the velocity?
- If the water depth is only 50 meters, what is the velocity?
- Is this faster or slower than a deep water wave?
- If the velocity is 15 meters per second, what is the depth of
the water?
|
|
| |
VOCABULARY
- velocity: speed or the rate of action.
- wave length: is the distance between two successive wave crests
- wave period: is the time it takes two wave crests to pass a
fixed point.
|
|
| |
SOURCE
- Adapted from 1998 "Project
Oceanography" Spring Series, Copyright, University of South
Florida Distance and Technology Mediated Learning
|
|