|
|
MATERIALS
- 2 lab thermometers, graduated in Fahrenheit and/or Celsius scale
- empty milk container or box
- piece of cotton or cotton shoelace
- kite string or sewing thread
- field journal
|
|
| |
PROCEDURE
|
|
| |
|
|
Activity
- Attach the cotton ball or piece of the shoelace to the bulb
of one thermometer. The wet bulb is the thermometer with the cotton,
the dry bulb is the thermometer without cotton.
- Attach both thermometers to the side of the milk carton or box
by securing it with the thread or string.
- Wet the cotton with clean room temperature water.
- Immediately take temperature readings of both thermometers.
- Record the temperatures in journal.
- Take temperature readings of each thermometer after one minute.
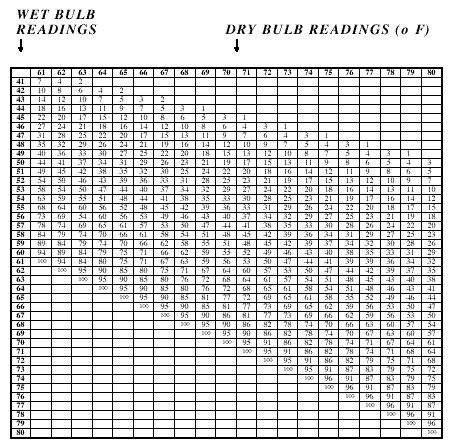
- Using the attached chart, determine the relative humidity.
|
|
| |
Footnote
- It may be necessary to fan the thermometers for the one minute
period to allow for a greater volume of air to reach the thermometer
bulbs and achieve a more accurate reading. If your thermometers
give Celsius readings only, the conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit
is:
°F= (1.8 x °C) + 32
|
|
| |
Assessment Ideas
- Help the students practice using the Relative Humidity chart
(provided below).
- Students should keep a log of readings in journals or on spreadsheet
files.
- Create graphs using paper and pencil or computer spreadsheets
can be created.
|
|
|
|
| |
CROSS-CURRICULAR IDEAS
- Mathematics: Data can be entered into a spreadsheet and relative
humidity readings can be taken at various times in the day and during
an extended period.
- Social Science: Students should consult local newspapers for
weather forecasts and compare/contrast the relative humidity readings
they have computed and those that have been published.
|
|
| |
VOCABULARY
- evaporation: the conversion of liquid to vapor due to heat.
- hygrometer: one of many instruments used to measure relative
humidity.
- relative humidity: the amount of water vapor present in the
air compared with the maximum amount of moisture that the air can hold
at that temperature.
- sling psychrometer: a device used to determine the dry and
wet bulb temperature of the air. It consists of two thermometers mounted
on a piece of metal that swings rapidly in the air for several minutes
to achieve the required degree of wet bulb cooling.
|
|
| |
SOURCE
- Adapted from "Winds of Change" educational CD-ROM, Copyright
Caltech and NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory
|
|