|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOXIC DINOFLAGELLATE BLOOMS: Toxins that affect ion
channels
|
|
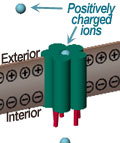
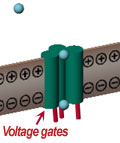
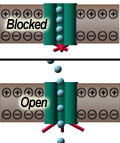
Below at left, the resting cell's
interior has a slight negative charge (-) relative to its
exterior. Changes in voltage across the membrane can open
and close voltage gates to control the flow of positively-charged
(+) ions toward the cell's interior. Such flow occurs to achieve
equilibrium across the membrane in terms of electrical charge and
ion concentration. Some algae-derived toxins bind to these
channels, blocking ions from flowing into cells. Other toxins
have the opposite effect: they bind to these channels, keeping them
open and promoting higher-than-normal ion flux.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ciguatoxin binds to the sodium
channel and promotes sodium ion (Na+) influx by keeping sodium channel
open. Maitotoxin keeps calcium channels open,
promoting calcium ion influx (Ca++). Ciguatoxin behaves similarly
to brevetoxin (below), although the molecules are structurally
different.
|
|
|
|
|
Brevetoxin binds to the sodium
channel, keeping it open and helping to promote sodium ion
(Na+) influx. Although different in molecular structure from ciguatoxins
(above), the effect on the sodium channel is similar. Also,
the effect of brevetoxin on the sodium channel is opposite that
of saxitoxins (below).
|
|
|
|
|
The positive charge on part of
the saxitoxin molecule allows it bind to and block the sodium
channel, inhibiting the passage of sodium ions (Na+); this causes
muscles to relax and may lead to respiratory
failure or death.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOXIC DINOFLAGELLATE BLOOMS:
Toxins that inhibit proteins
|
|
|
|
Inhibits the proteins (phosphatase
1 and 2A) that control sodium secretion by intestinal cells, thereby
causing nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and
diarrhea in humans. Chronic exposure to these toxins has also
been suggested to promote the formaton of digestive tract tumors,
although the mechanism hasn't been identified.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domoic acid (DA) is similar in
structure to amino acid which communicates messages among neurons
in the central nervous system (glutamic acid). However, DA overstimulates
the neurons in the brain's hypocampus until these cells start to
die. DA also keeps the calcium channels open in nerve and
muscle cells (as depicted above).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |